2020 and 2021 have been the years of excuses. When it comes to day-to-day life, the lockdowns took away the option for in-person socialization. Despite everyone being locked inside, that same excuse is being applied to vehicle inventories - both new and used. That isn’t the whole story though. The other word being thrown around these days is semiconductor or chip shortage. While you may be aware that we are seeing exceptionally high trade-in values and record low inventory levels, the “why” isn’t talked about as much.
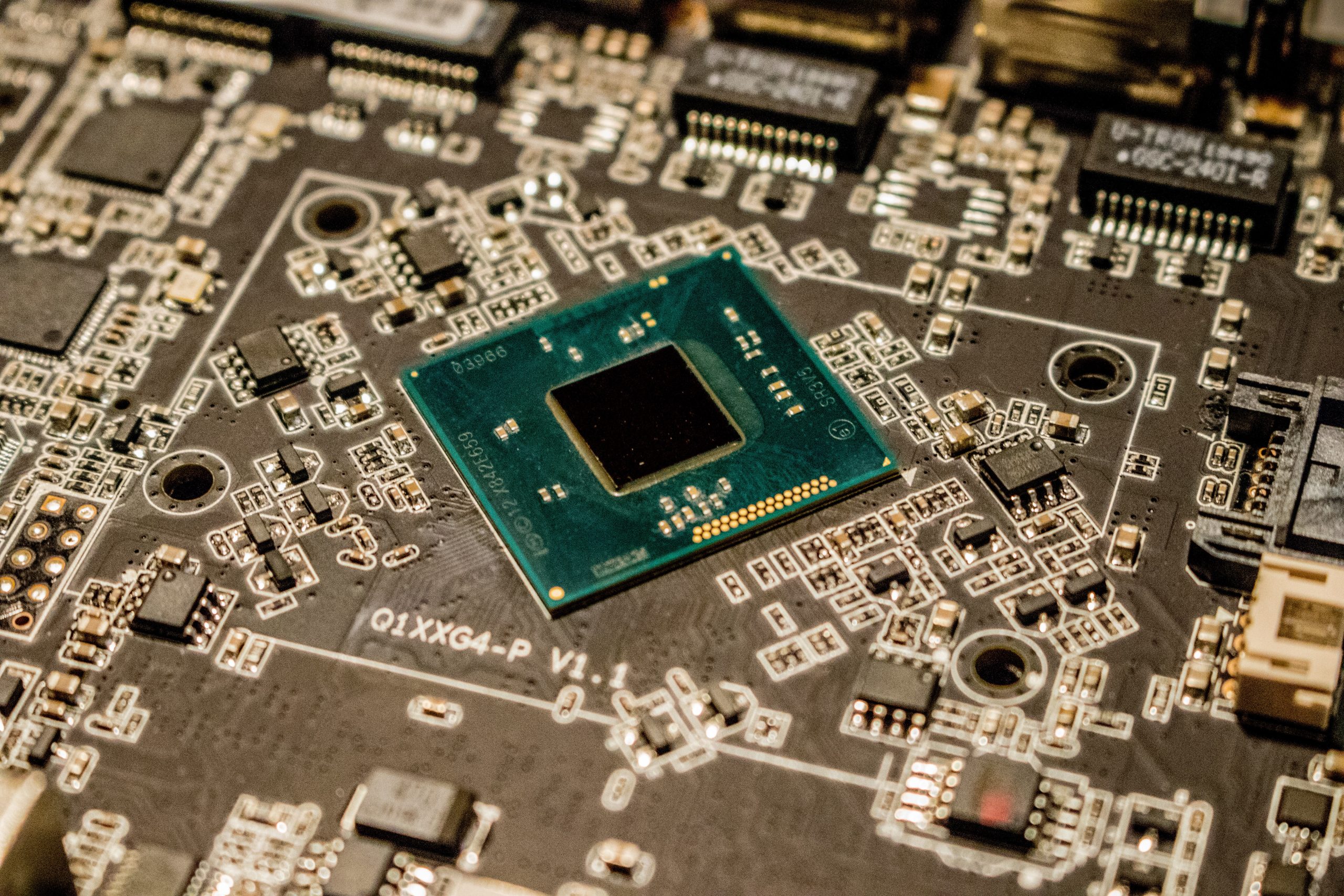
Let’s start with the basics: what is a semiconductor? If you can recall your science classes, you may remember that a conductor allows electricity to pass through it. The semi part is critical too. Unlike a normal conductor, there are a few insulator tendencies to a semiconductor that means electricity doesn’t flow quite as easily as it would if it were a traditional conductor. Currently, semiconductors are produced from silicon and power the connected world around us.
What are semiconductors used in? The better question is what aren’t they used in? When we say they are used in the connected world around us, we mean if the device connects to the internet or needs electricity to work — whether it be your smartwatch, your phone, or your tv remote — there is a semiconductor somewhere inside. Depending on the device, there may be more than one. Some new cars can have more than 100!
Back to those excuses. When the world shut down, many people didn’t stop working. Instead, they had to create their own home office set up including increasing their wifi, buying new computers for home and possibly other things along the way to make working and living at home more fun. Virtually overnight the demand for semiconductors went through the roof. However, many auto manufacturers were forced to shut down and anticipated a market slowdown. That anticipated slowdown caused them to cancel their orders for semiconductors and didn’t quite come to fruition. Now, the raw materials (Quartz which is mined to get the silicon) were just as easy to come by last year as they were years prior. It is the manufacturing process that became an inhibitor.
A car manufacturing plant takes downtime for a couple of weeks to retool plants for the next model year. When it comes to increasing production or adjusting the manufacturing processes for semiconductor chips, the process is a lot more time-consuming and expensive. Throw in a massive increase in demand for consumer electronics and auto manufacturers bouncing back sooner than expected and you have a semiconductor shortage on your hands. Throw in some natural disasters and all of a sudden you have waitlists left, right, and center.
When it comes to the automotive industry, we mentioned that some vehicles can use upwards of 100 semiconductors. So, what are semiconductors used for? A few years ago, the list might have been relatively short, but as cars become driving computers we come back to the same question: what aren’t semiconductors used for? The industry’s move to electrification demands semiconductor usage, as does the continual addition of features like adaptive cruise control and head-up display. One of the most helpful features — up-to-date traffic reports — requires semiconductors to stay connected in real-time. From engine performance to touch screen interfaces, a semiconductor is integral to delivering a 21’st century vehicle.
So where does that leave us? In one of the most unusual automotive markets anyone has seen. Whether you are considering selling your vehicle or taking advantage of low interest rates on a new one, it is a completely different experience than it was even just a year ago.